শ্বাসনালী ও ফুসফুস (Chest / Asthma)
অ্যাজমা ও শ্বাসকষ্টের চিকিৎসায় দক্ষ চিকিৎসকরা — শ্বাসনালীর সমস্যা দ্রুত শনাক্ত করে সুচিকিৎসা প্রদান করেন।
- প্রধান লক্ষণ: কাশি, হাঁপানি, শ্বাসকষ্ট।
- কবলার জন্য দেখাতে হবে: ঘণ্টাব্যাপী কাশি বা শ্বাসকষ্ট।

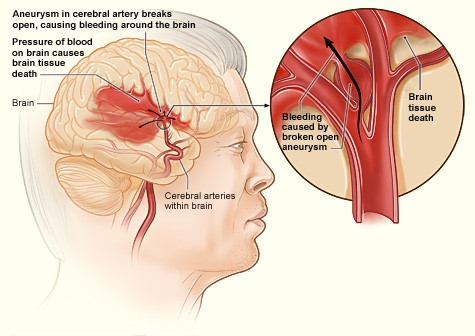
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of your brain is interrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by blood, brain cells begin to die within minutes. Understanding the causes and risk factors can help you prevent a stroke.
Strokes occur in two main ways: blood flow to the brain is blocked, or there is bleeding in the brain.
1. Ischemic Stroke:This type accounts for 8 out of 10 strokes. It happens when a blood vessel carrying blood to the brain gets obstructed, often by fatty deposits in arteries breaking off and traveling to the brain, or by a blood clot formed due to irregular heartbeat.
2.Hemorrhagic Stroke: Although less common, this type can be more serious. It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts or leaks. Uncontrolled high blood pressure and excessive use of blood thinners can lead to hemorrhagic strokes.
Several conditions and lifestyle choices can increase your risk of stroke. Some risk factors are treatable, while others are beyond your control:
1. High Blood Pressure: Also known as hypertension, this is the leading cause of strokes. Blood pressure readings consistently at 140/90 or higher warrant medical treatment.
2. Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco increases stroke risk. Nicotine raises blood pressure, while cigarette smoke promotes fatty deposits in neck arteries and thickens the blood, increasing clot likelihood. Even secondhand smoke can be harmful.
3. Heart Disease: This includes defective heart valves and atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat), responsible for a significant number of strokes in the elderly. Clogged arteries due to fatty deposits also contribute.
4. Diabetes: Diabetics often have high blood pressure and are more likely to be overweight, both of which elevate stroke risk. Diabetes damages blood vessels, further increasing stroke likelihood. High blood sugar levels during a stroke can worsen brain damage.
5. Weight and Exercise: Being overweight can raise stroke risk. Regular physical activity, like a daily brisk 30-minute walk or muscle-strengthening exercises, can help reduce this risk.
6. Medications: Some drugs, such as blood thinners, can increase stroke risk by causing bleeding. Hormone therapy for menopause symptoms and low-dose estrogen in birth control pills have also been linked to higher stroke risk.
7. Age: While anyone can have a stroke, the risk increases with age, doubling every decade after age 55.
8. Family History: Strokes can be hereditary, as high blood pressure or diabetes tendencies can run in families. Some genetic disorders that block blood flow to the brain can also cause strokes.
9.Gender:Men are slightly more likely to have a stroke than women of the same age. However, women tend to have strokes at older ages, leading to a higher likelihood of severe outcomes and mortality.
10.Race: African-Americans and nonwhite Hispanic Americans have a higher incidence of strokes than other groups in the U.S. Sickle cell disease, more common in these populations and those with Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, or Asian ancestry, can narrow arteries and disrupt blood flow, increasing stroke risk.
এখন ঘরে বসে সকল বিশেষজ্ঞ ডাক্তারের সিরিয়াল দিতে উক্ত হটলাইন নাম্বারে কল দিন: 01763-818283 নির্দ্বিধায় গ্রহণ করুন আপনার এবং আপনার পরিবারের জন্য সেরা স্বাস্থ্য সেবা সমাধান ।
Doctor All Khulna is a trusted health information platform that helps you find the best doctors, hospitals, and clinics in Khulna. We provide verified details about medical specialists, chamber locations, visiting hours, and contact numbers to make your healthcare journey easier and faster.
At Doctor All Khulna, our mission is to connect people with the right healthcare professionals in Khulna city. Whether you are looking for a general physician, medicine specialist, or dentist, we ensure that you get accurate and updated information in one place.
Searching for the best doctors in Khulna? Doctor All Khulna lists top-rated specialists from different fields such as medicine, cardiology, gynecology, pediatrics, dermatology, and more. Each profile includes qualifications, experience, and patient-friendly details.
Doctor All Khulna saves your time and effort by bringing together all healthcare-related information for Khulna residents. You can explore doctor profiles, hospital details, and consultation schedules — all in one convenient, mobile-friendly website.
With Doctor All Khulna, you can easily search for doctors near your area. Our smart search system helps you find specialists by location, hospital name, or category — ensuring you always reach the right doctor in Khulna at the right time.
Our goal is to make quality healthcare information accessible to everyone in Khulna. Doctor All Khulna aims to become the most reliable source for finding medical professionals and healthcare services across the city.
Doctor All Khulna not only helps you discover experienced doctors but also keeps you informed with the latest health tips and medical news in Khulna. Our platform is designed to guide patients toward trusted healthcare services, so you can make confident decisions about your treatment and wellness.
Whether you need a specialist for diabetes, heart disease, pregnancy care, or skin problems, Doctor All Khulna gives you access to genuine doctor profiles and hospital details. We continuously update our listings to ensure that you always receive the most accurate and reliable medical information.
Doctor All Khulna is built with the people of Khulna in mind — helping families find affordable and quality healthcare without confusion. Our goal is to simplify the process of finding doctors, booking consultations, and learning about different medical specialties all in one place.
Through Doctor All Khulna, we aim to create a bridge between patients and healthcare providers. By improving access to verified information, we make healthcare in Khulna more transparent, accessible, and trustworthy for everyone living in the city.
If you are searching for the best gynecologist in Khulna, Doctor All Khulna is here to help you find trusted and experienced female health specialists. Our platform lists qualified gynecology and obstetrics doctors who provide expert care for women’s health, pregnancy, fertility, and reproductive wellness.
At Doctor All Khulna, we ensure that patients receive accurate information about gynecologist chambers, consultation times, hospital locations, and appointment details. Whether you need regular checkups, prenatal care, or treatment for women’s health issues, you can easily find the right gynee doctor in Khulna through our verified listings.
Our goal is to make women’s healthcare in Khulna more accessible and transparent. Doctor All Khulna connects you with compassionate and skilled doctors who prioritize comfort, privacy, and long-term wellness for every woman.
অ্যাজমা ও শ্বাসকষ্টের চিকিৎসায় দক্ষ চিকিৎসকরা — শ্বাসনালীর সমস্যা দ্রুত শনাক্ত করে সুচিকিৎসা প্রদান করেন।
নতুন আঘাত বা বারবার মাথা ব্যথা, স্মৃতি কমে গেলে নিউরোলজিস্ট দেখুন — দ্রুত ডায়াগনসিস ও মেডিকেল প্ল্যান পাওয়া যায়।
রিউমাটিক ও আর্থ্রাইটিসের জটিলতায় বিশেষজ্ঞ — দীর্ঘমেয়াদী ব্যথা ও হাঁটার সমস্যার ক্ষেত্রে সহায়তা করে।
কিডনি, প্রস্রাবের সমস্যা ও পুরুষদের শ্রোণিবৃত্তীয় রোগের নির্ণয়ে দক্ষ ইউরোলজিস্ট।
কান-নাক-গলা সংক্রান্ত সমস্যা: শ্রবণহ্রাস, ভয়েস চেঞ্জ, গলা ব্যথা — দ্রুত পরীক্ষা ও চিকিৎসা।
Top 10 ENT Specialistsমাথা বা স্নায়ু-শল্যচিকিৎসা প্রয়োজন হলে নিউরো-সার্জনির কাছে যান — জটিল কেসের দক্ষ ব্যবস্থাপনা।
Top Neurological Specialistsহৃদরোগ, ব্যথা/বুক চাপে দ্রুত কার্ডিওলজিস্ট দেখুন — ডায়াগনসিস ও ম্যানেজমেন্ট গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
Top 10 Heart Specialistsকিডনি বিশ্লেষণ, ক্রনিক কিডনি ডিজিজ ও ডায়ালিসিস সম্পর্কে পরামর্শ।
Top 10 Kidney Specialistsশিশুর বৃদ্ধি, টিকাদান এবং সংক্রমণজনিত সমস্যা—বিশেষজ্ঞ শিশু-চিকিৎসক (Paediatrician)।
Top 10 Child Specialistsঅন্তর্বর্তী চিকিৎসা, জটিল রোগের মেডিক্যাল ম্যানেজমেন্ট ও রেফারেল — অভিজ্ঞ মেডিসিন বিশেষজ্ঞ।
Best Medicine Specialistsলিভার সংক্রান্ত সমস্যার দ্রুত সঠিক ডায়াগনসিস ও কেয়ার প্রয়োজন।
Top 10 Liver Specialistsজটিল অপারেশন ও ইমার্জেন্সি সার্জারি — অভিজ্ঞ সার্জনরা নিরাপদ অপারেশন প্ল্যান দেন।
Top 10 Surgery Specialistsরক্তে সুগারের নিয়ন্ত্রণ, জীবনযাত্রার পরামর্শ এবং দীর্ঘমেয়াদী ব্যবস্থাপনা।
Top 10 Diabetes Specialistsঅস্থি ও জয়েন্ট ইনজুরি, ট্রমা এবং অর্থোপেডিক সার্জারির জন্য বিশেষজ্ঞ।
Top 10 Orthopedic Specialistsগাইনেকোলজিস্ট ও প্রসূতি বিশেষজ্ঞ — গর্ভস্থ পর্যবেক্ষণ, রুটিন চেকআপ ও জরুরি কেস।
Top 10 Gynecologistsগ্যাস্ট্রোলজিস্টরা হজম তন্ত্র, আলসার ও লিভার ইনফেকশনের সঠিক চিকিৎসা করে থাকেন।
Liver & Gastrology Specialistsট্রমা কেয়ার, ফ্র্যাকচার ম্যানেজমেন্ট ও রিকনস্ট্রাকটিভ সার্জারি।
Orthopedic & Trauma Doctorsলোকাল মেডিসিন ডক্টরদের ডিরেক্টরি — অ্যাপয়েন্টমেন্ট এবং ডাক্তারদের প্রোফাইল।
Medicine Specialist Doctors